4.3.13.1. Groupings
IRM has a general-purpose mechanism called Groupings that allows IRM Users to create collections of Managed Objects from different Super Categories in a single Grouping object. Groupings can be created purely for organizational purposes and/or for permissions-related administrative purposes.
For example, Groupings can be created to represent organizational structures within a company e.g. Divisions, Departments, Business Units, Teams etc., or installed infrastructure systems, such as: Horizontal Plant, OSP, Risers, Windows Servers, Web Servers, etc.
Managed Objects can then be assigned to these Groupings as an indication of ownership (e.g. this division owns this equipment), membership (this user works in this team), Administrative control (this department administers this cabling), or some other relationship.
There are several ways in which an object can be included in a Grouping. For a detailed description of each way, click on the Overview Grouping section.
The following screenshot images and text explain the main parts of the General tab of the Grouping Properties dialog, which is the main interface for managing Groupings in IRM.
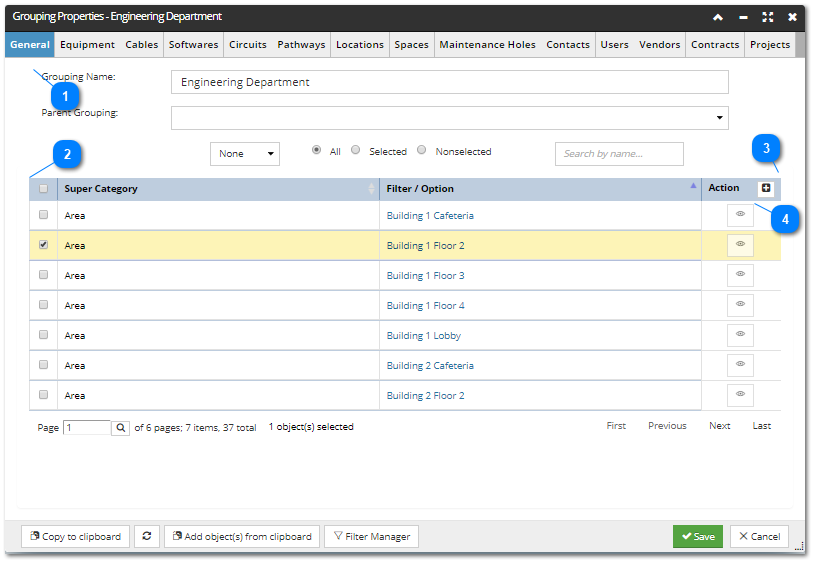
|
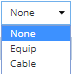
The + Action button in the opens a drop-down menu listing available Super Categories, which enables the user to select the Super Category within which a new Filter will be defined:
 Selecting any of the Super Categories (except the Grouping), opens the appropriate Filter Properties dialog, where the user can specify the filter criteria that will be used to auto-assign the specific managed object(s) into the Group.
If the Groupings Super Category is selected, another instance of Grouping Properties opens, displaying a valid list of groupings allowing the user to assign object to this Grouping based upon the objects returned are assign to another Grouping.
For Example, let's assume you already have 2 groupings defined, named Copper Backbones and Fiber Backbones, which returned only the Equipment and Cables associated with each specific infrastructure. You could define a New Grouping named All Risers and just assign the two existing Groupings named Copper Backbones and Fiber Backbones to the All Risers grouping.
Grouping is valid if it doesn't violate agreed hierarchical structure of groupings. For more details on this, click on the Overview Grouping section.
|
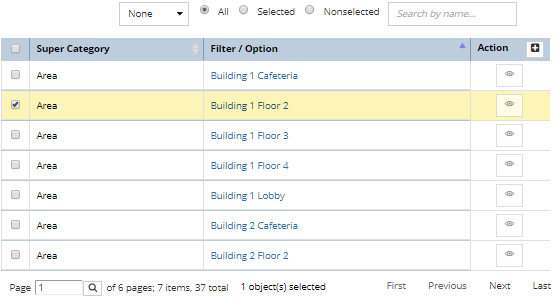
Other tabs in the Grouping Properties dialog are each dedicated to one of the Super Categories whose objects can be included in a Grouping object. Each of these tabs display similar columns for each instance, like Name, Type, Categories, Vendors, Contacts, etc.
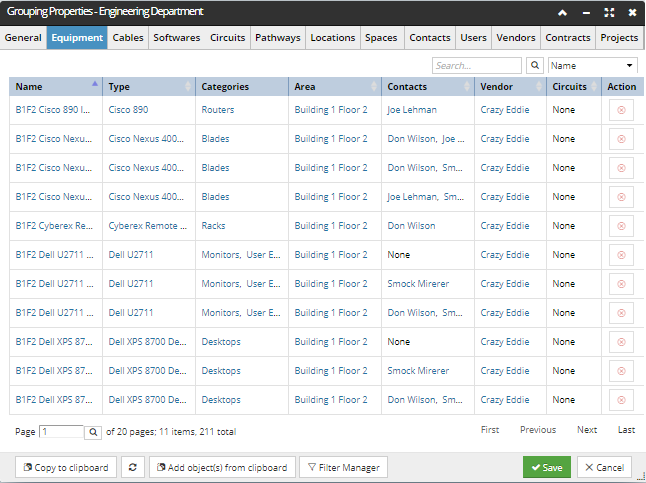
Note: Additionally, a Quick Search feature allows the user to easily search through the list based on column data:
IMPORTANT: if the object being copied is directly assigned to a grouping by copy and paste and not by filter, then when its duplicated the assigned copy and pasted groupings are persisted on the duplicated object. To put simply, the duplicated object is also assigned to the Grouping.