Geospatial Data
Spatial management in Planet IRM is done in Areas - an Area defines a physical plane in which objects are placed and arranged using a visual editor. Each Area has an associated Coordinate System object that defines the parameters of the plane and geo references.
The main parameters of a Coordinate System are:
-
Units (inches, centimeters, feet, meters, etc.)
-
Geo Marker - special data that defines the relation of a particular point in the Area to a particular geographic location
-
GIS - a Cartesian coordinate system that is a projection of the globe and which allows its own (Cartesian) coordinates to be transformed to and from geo coordinates (latitude and longitude)Note: geo-referenced alignment uses a GIS Coordinate system; the user can pick which GIS system to use in case the default one is not correct.
Selecting which GIS system to use is done in the Coordinate System Manager and Coordinate System Editor (shown below) dialogs.
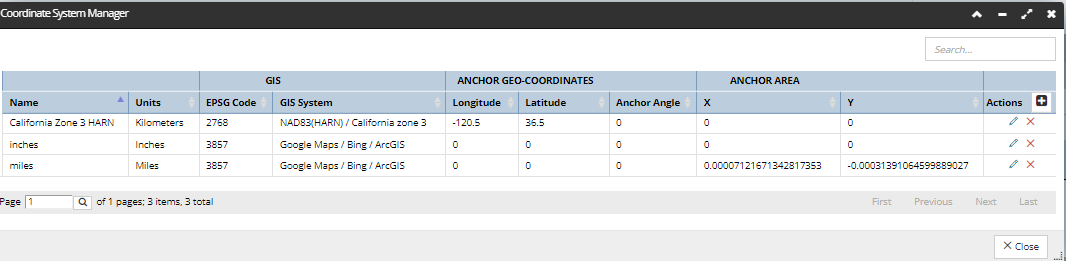
A GIS is comprised of the following information:
-
EPSG Code- a code number that gives the GIS a standardized name
-
proj4String - parameters to PROJ.4 that describe the geo coordinate system
-
Projection Variety - Mercator, LCC, Other
-
geo Bounding box.
The user cannot add new GIS objects, but IRM supports a large number of them by default including all of the most useful ones for outside plant work. The user needs only select one from the pre-defined list, as seen in the following screenshot image:
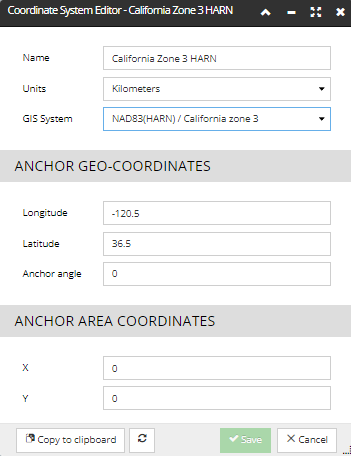
WARNING: In case users select an incorrect GIS for their data, they will have map alignment problems and/or incorrect lengths for Cables and/or other potentially difficult-to-diagnose problems. Therefore care should be taken to use the best GIS.
The user needs to be aware of what kind of geospatial coordinates are in a given Area or CAD file, as well as shapefile coordinates, which are sometimes in geodetic coordinates (latitude and longitude) and as such are not translated to Cartesian coordinates as they must be for the software to work correctly.
WARNING: IRM allows a single Area to support a single GIS Coordinate system - be aware that you cannot mix different Coordinate systems. When importingCAD or Shape files, their coordinates are translated to the coordinates of the Area.
The following subtopics explain in detail how to perform the following Geo Coordinate-related operations: