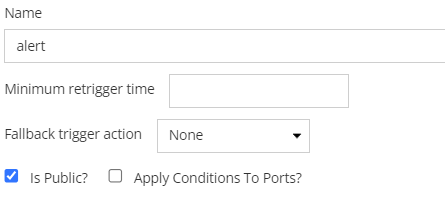
4.2.2.3. Manager dialogs
In IRM there are many convenience features that enable defining and managing configurations which can be applied to specific objects or other parts of the application.
Some of the Dialogs that use this concept are:
-
Filter Manager,
-
Analytics Manager,
-
Layer Manager,
-
Grid Configuration Manager
The general idea is that the dialog allows managing (add / delete / edit / control visibility to) a list of configuration objects. The general layout for all Manager dialogs can be explained through using the example of the Analytics Manager dialog:
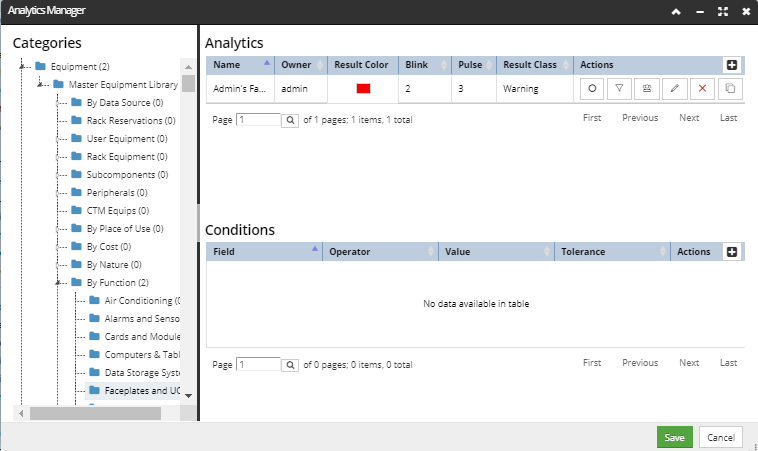
Like most Manager dialogs, Analytic Manager has several common controls:
-
Categories tree - located at the left part of the dialog. Tree controls are as previously described.
-
Configurations grid - each row displays a configuration entry and its basic properties, along with additional standard (Manager) action buttons:
 - Apply / don't apply configuration - enabled for all configurations
- Apply / don't apply configuration - enabled for all configurations - Public configuration - visible and editable for everybody. Only the user who created it, or Admin users can delete it or change its privacy status.
- Public configuration - visible and editable for everybody. Only the user who created it, or Admin users can delete it or change its privacy status. - Private configuration - only the user who created it, or Admin users can see or edit it. Users specifically selected as Viewers for this config can also see and run it, but cannot edit or delete.
- Private configuration - only the user who created it, or Admin users can see or edit it. Users specifically selected as Viewers for this config can also see and run it, but cannot edit or delete. - Edit configuration - opens Configuration Editor dialog (see next dialog type). Public configurations can be edited by everybody. Private configurations can be edited if owned by a current user or by Admins.
- Edit configuration - opens Configuration Editor dialog (see next dialog type). Public configurations can be edited by everybody. Private configurations can be edited if owned by a current user or by Admins.  - Remove configuration - enabled if owned by a current user or for Admins.
- Remove configuration - enabled if owned by a current user or for Admins.  -Copy / Clone / Duplicate configuration - creates a duplicated configuration that has a Copy appended to the name
-Copy / Clone / Duplicate configuration - creates a duplicated configuration that has a Copy appended to the name - Create new configuration- opens Configuration Editor dialog with default / empty parameters
- Create new configuration- opens Configuration Editor dialog with default / empty parameters
The standard Save and Cancel buttons enable saving or discarding any changes made to the configurations and close it.
Public and Private configuration in IRM Managers.
As mentioned earlier, the Manager dialogs allow managing (adding / deleting / editing / controlling visibility to) a list of configuration objects, which can be made either public or private.
Privacy for configurations has everything to do with ownership of said configurations or even files. A user who created the original configuration becomes an owner of it, and gains an ability to view, edit, delete or change privacy settings for this configuration.
Public configurations can also be viewed or edited by other users, though they would not be allowed to delete this configuration or change its privacy settings.
Private configurations are hidden from other users, unless they were specifically added to Viewers list for this configuration. In this case, Viewers will be able to see it and run the associated report, provided they also have access to objects in this configuration (like Areas or Spaces), but not edit or delete it.
Also note that Admin users can also see or edit both public and private configurations, even not being an owner of them. This is an intentional component of our system. We use it as an effective compromise between safety and cooperation, to avoid the possibility of creating inaccessible files or configurations, should their owners be deleted from our system.
Here are some example snapshots from various managers, illustrating how you can switch between private and public status.
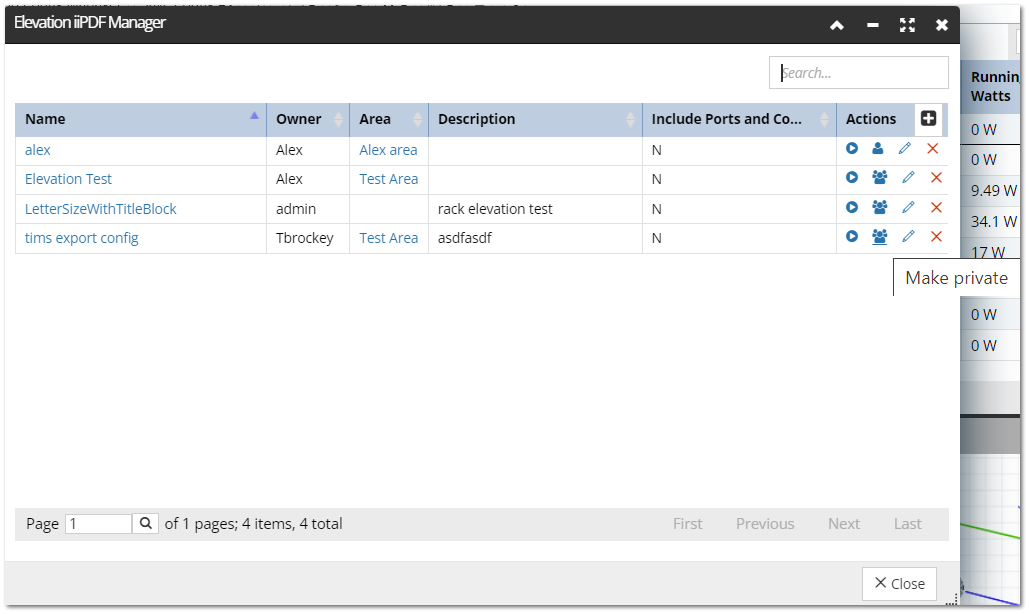
By clicking on  or
or  you can switch between private and public status.
you can switch between private and public status.
In some IRM managers you can switch the status by simply pressing the  and checking or unchecking the is public? box as shown below.
and checking or unchecking the is public? box as shown below.